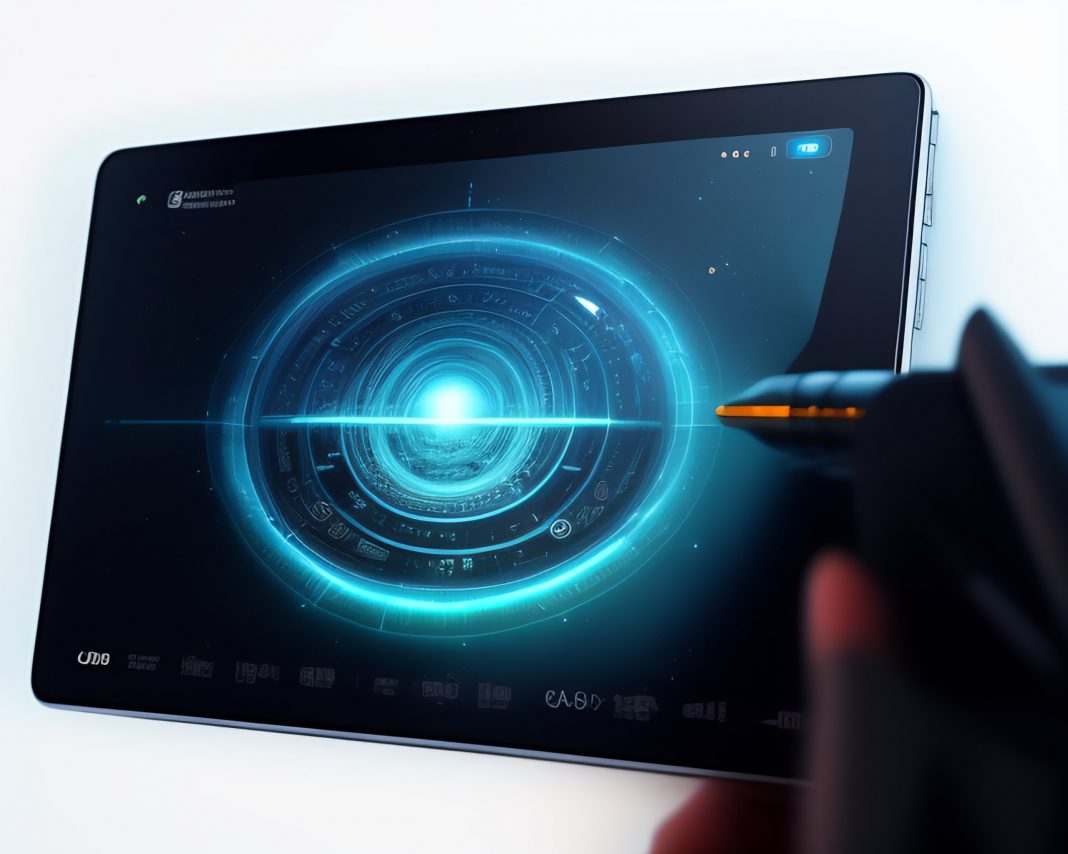
Biometric technologies have become an innovative means of protecting sensitive data in an age where digital security and seamless identification are vital. Iris scanning stands out among these technologies as a model of innovation, providing a fresh method of identification that is extraordinarily safe and accurate.
With its intricate patterns and vibrant hues, the iris is a natural key that sets each individual apart. Unlike traditional methods that rely on easily forgeable elements like passwords or PINs, the iris is an authentication factor that cannot be replicated or shared. It’s a technological marvel that taps into the very essence of human individuality.
As technology continues to evolve, future applications of iris scanning are being explored beyond its current use cases. Possibilities range from enhancing security measures in online transactions and securing sensitive data in various industries. Imagine a scenario where your iris becomes your key to accessing your accounts at Slots Capital Casino, making transactions safer and simpler.
Historical Context of Iris Scanning’s Development
The journey of iris scanning’s development traces back to the pioneering work of ophthalmologist Frank Burch in 1936. Burch’s visionary insight into the iris’s uniqueness set the groundwork for a revolutionary concept: the iris could serve as an unalterable identifier.
From Burch’s hypothesis to the reality we have today is marked by milestones of innovation and perseverance, epitomized by John Daugman’s algorithm for iris detection in the 1990s.
Scanning evolved from a visionary notion to a cutting-edge biometric method integrated into various industries, from security and access control to mobile devices and border checkpoints.
The developments starting with retinal authentication and bringing us to the sophisticated iris scanning technology we know today demonstrates the persistent drive of innovators to enhance security, privacy, and efficiency in the realm of identification and authentication.
Accuracy of Iris Scanners
Central to the accuracy of iris scanning is the use of the iris’ distinct biometric characteristics for identification. This contrasts with fingerprint verification, which employs a significantly smaller number of key points.
The iris scanning process captures around 260 anchor points, a comprehensive set that further bolsters its accuracy. Attempting to forge identification through iris scanning is exceptionally daunting due to the iris’ unique reflective properties.
This feature, often overlooked, plays a pivotal role in adding an extra layer of security. The complex interplay of these attributes renders replicating another person’s iris virtually impossible, making iris scanning an exemplary safeguard against identity fraud.
Mitigating Health Concerns with Infrared Radiation
Although iris scanning technology provides ground-breaking identifying capabilities, questions have been raised about the impact of infrared (IR) radiation on the eyes. Manufacturers have actively responded to these worries by reducing potential risks.
These precautions include regulating the distance between the radiation source and the eyes, reducing the intensity and wavelength of IR light, and ensuring exposure times are minimal.
Manufacturers are improving the iris scanning process’ accuracy and putting user safety first by following these safety regulations, which reaffirms the technology’s dedication to security and user safety.
The Process of Iris Scanning
Iris scanning, a marvel of biometric technology, unfolds in a carefully orchestrated two-stage process that harnesses the unique patterns within the iris to establish secure and accurate identifications. This process involves capturing the intricate details of the iris, followed by a meticulous comparison that verifies the authenticity of the scanned data.
If a match is identified between the newly generated iris code and an existing code within the database, the individual is positively identified, granting access or authentication. Conversely, if a match cannot be found, the individual’s identity is not confirmed, highlighting the technology’s capacity to detect attempted forgeries or unauthorized access.
Applications of Iris Scanning
Here are some of the current applications of iris scanning:
- Airport Security: Airports around the world are adopting iris scanning as part of their security protocols. For instance, Dubai International Airport uses iris recognition for expedited immigration and security clearance, providing travelers with a swift and secure entry process.
- Border Crossings: Many countries are integrating iris scanning into their border control systems to enhance immigration processes. The United Arab Emirates, for example, uses iris recognition at its border checkpoints to facilitate smooth and secure entry for residents and visitors.
- ATM Transactions: Some banks have introduced iris scanning as an additional layer of security for ATM transactions. Customers can use their eyes to authenticate their identity before performing financial transactions.
- Patient Identification: In healthcare settings, iris scanning helps prevent medical identity theft and improves patient safety. Hospitals and clinics use this technology to accurately match patients with their medical records, reducing the risk of errors.
- Workplace Attendance: Iris scanning is used by some companies to track employees’ attendance accurately. This eliminates time fraud and provides a secure and convenient method for clocking in and out.
- Refugee Registration: In refugee camps in Jordan, iris scanning helps efficiently register and track individuals, ensuring they receive the aid they need. This technology assists in managing large populations and preventing fraud.
Controversy and Ethical Considerations: The Worldcoin Case
Recent developments in the biometric world have introduced a contentious dialogue surrounding iris scanning technology. The Worldcoin initiative, which involves scanning individuals’ irises in exchange for cryptocurrency, has ignited a debate.
Critics have labeled this endeavor bribery and raised concerns about surrendering biometric data to a for-profit startup with uncertain motives. The controversy surrounding Worldcoin underscores the ethical difficulties associated with biometric data and prompts important questions about consent, ownership, and potential misuse.
Balancing Potential and Privacy
The promise of iris scanning, exemplified by its integration into various industries and the potential for secure and frictionless interactions, is juxtaposed against the inherent concerns about privacy, security breaches, and surveillance.
While Worldcoin asserts that biometric data is processed and converted into cryptographic code before deletion, the history of data mismanagement in Silicon Valley has left a skeptical audience wary of such assurances. The debates sparked by Worldcoin remind us that as we embrace the future of biometric technology, we must navigate the delicate balance between technological advancement and safeguarding individual rights.
The journey of iris scanning is far from over. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the applications and benefits of this remarkable biometric identifier. Embracing iris scanning is not merely an adoption of technology; it’s a recognition of the symbiotic relationship between human ingenuity and scientific advancement.
































 Online casino
Online casino
