NFC stands for Near Field Communication.It is a short-range wireless technology that allows devices to communicate with each other when they are brought within 4cm or less of one another. This technology traces its origins back to radio-frequency identification (RFID), which was first patented in 1983 by Charles Walton. NFC started gaining attention in 2002 and was approved as an ISO/IEC standard in 2003.
The first NFC-enabled phone, the Nokia 6131, was released in 2007. Android produced its first NFC phone, the Samsung Nexus S, in 2010. Since then, NFC adoption has grown steadily, especially in Europe, Asia and Japan.
Contents
How NFC Works
NFC works through electromagnetic radio fields. One device, the initiator, generates a radio frequency field that can power a passive target, like an NFC tag or card. The initiator then modulates the field to send data to the target, which loads the modulated signal to respond back with data. This allows the two devices to exchange information.
Android devices can act as both NFC initiators to read NFC tags, and as targets to allow other devices to read data from them or exchange data between two Android devices.
NFC can operate in three modes:
- Reader/Writer mode: Allows the NFC device to read and write data to NFC tags and stickers.
- Peer-to-Peer mode: Enables two NFC devices to communicate directly with each other to exchange data. This is used by Android Beam.
- Card Emulation mode: Allows the NFC device to act as a contactless card that can be accessed by an external NFC reader. This is used for contactless payments.
NFC Capabilities on Android
Most modern Android devices come with built-in NFC support. This allows Android apps to leverage NFC to enable a variety of use cases:
- Contactless payments: Apps like Google Pay and Samsung Pay use the device’s NFC chip to emulate debit/credit cards for tap-and-pay transactions.
- Quick pairing: Tap two NFC-enabled Android devices to instantly pair them via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct.
- Data exchange: Beam content like contacts, web links, photos, videos between devices.
- Smart tags: Read embedded NFC tags to get more info about products, locations, etc.
- Access control: Use NFC stickers as secure keys to unlock doors, devices, apps.
Common Uses of NFC on Android
Some of the most popular uses of NFC on Android include:
- Mobile payments – Apps like Google Pay allow you to store your credit/debit card information and tap to pay at supported payment terminals.
- Transit/Event tickets – Many transit agencies and event organizers allow digital ticketing via NFC. Just tap your phone at the turnstile or entry gate.
- Bluetooth pairing – Tap two NFC-enabled Android devices to instantly pair Bluetooth accessories like speakers, headsets, etc.
- Content sharing – Apps utilize Android Beam to share contacts, photos, app links, web pages, and more by tapping devices.
- Smart home automation – Program NFC tags to configure your smart appliances and trigger custom actions.
- Access control systems – Office buildings can provide building access via NFC ID badges on employee phones.
How to Check for NFC Support
To check if your Android device supports NFC:
- Go to Settings => Connected devices
- Look for an option called NFC. If available, your phone supports NFC.
- Alternatively, look for the NFC logo (shown below) printed somewhere on your device.
If you don’t see the NFC options, your device does not support NFC unfortunately.
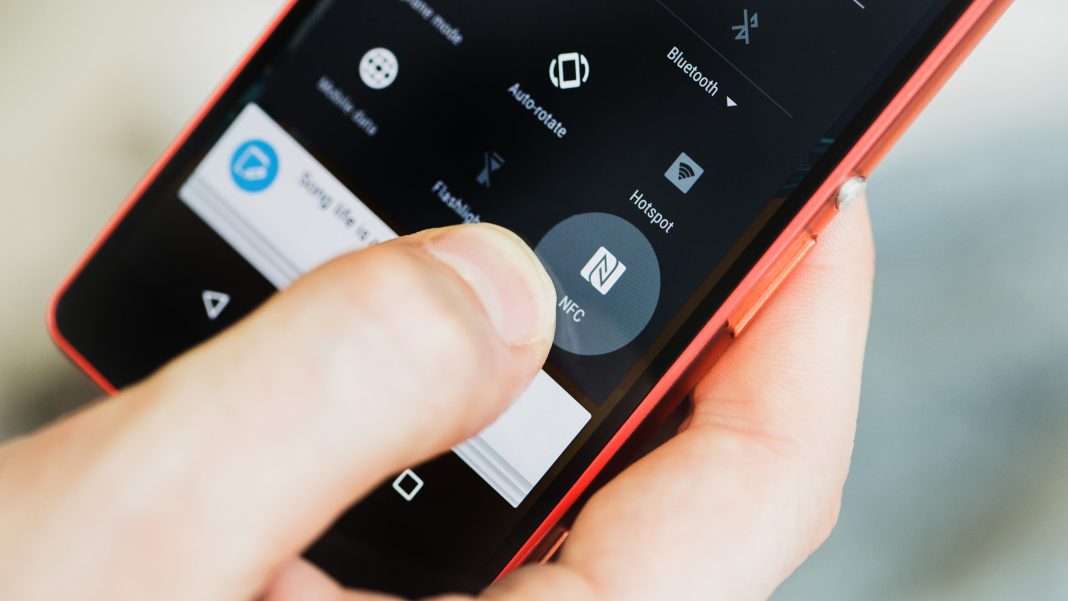
How to Enable NFC on Android
If your Android device supports NFC, make sure the NFC option is enabled:
- Go to Settings => Connected devices => NFC
- Turn on the switch next to NFC to enable it
- You may also see additional options to control NFC access and behavior
- Bring your phone near an NFC reader or another NFC device to use features like Android Beam
Once enabled, your apps and device can take advantage of NFC capabilities.NFC consumes very little battery so it’s generally safe to leave the feature enabled.
How Secure NFC Is on Android?
NFC is considered quite secure for the following reasons:
- Short range: Devices need to be within 4cm, making eavesdropping difficult.
- User initiation: Transactions require deliberate taps so accidental reads are rare.
- Encrypted data: Payment credentials are stored in a secure element and data is encrypted during transmission.
- To improve security, Android 10 introduced an option called Secure NFC.
However, some potential risks include:
- Session hijacking: Hackers replay intercepted payment data to make fraudulent transactions.
- Malware attacks: Attackers transfer malware apps via Android Beam.
- Location tracking: Tags covertly attached to track user locations without consent.
Conclusion
NFC is a short-range wireless communication standard that enables convenient contactless interactions between electronic devices. On Android, it facilitates use cases like contactless payments, content sharing, automations and access control. With proper precautions, NFC offers a fast and secure way to exchange data on the go.




































 Online casino
Online casino
