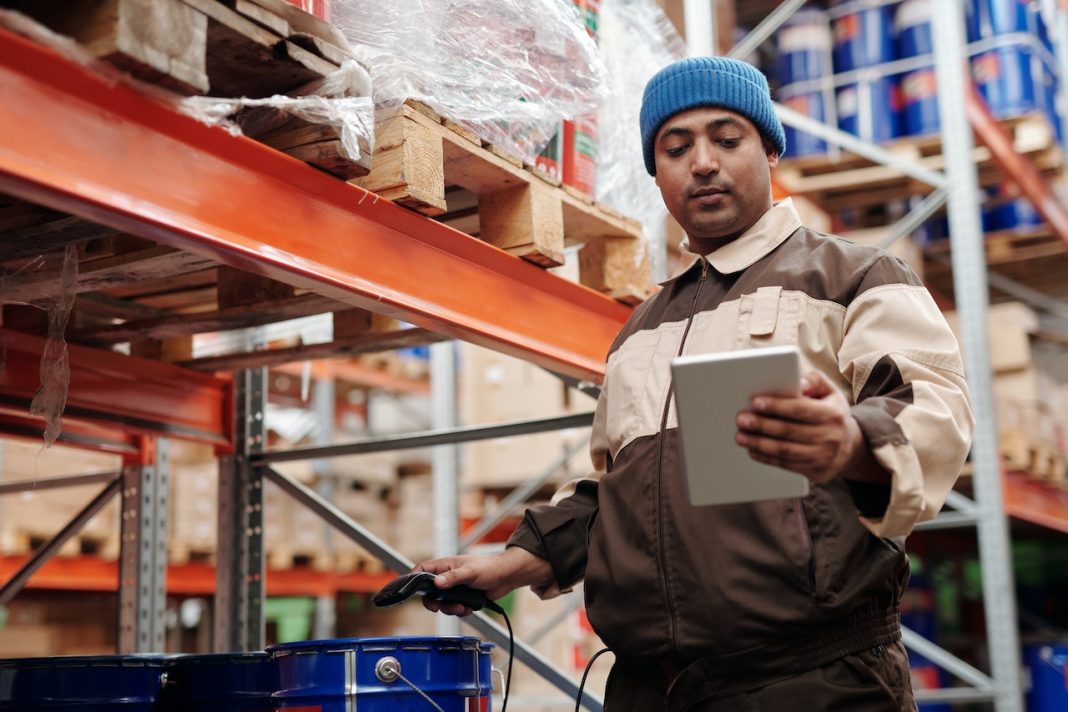
The logistics industry has undergone a revolutionary transformation, all thanks to warehouse automation. At the forefront of this revolution are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), which have become indispensable in optimizing operations. AGVs, these versatile warehouse sorting robots that can navigate on their own, are changing the system for small spaces by performing a range of tasks within warehouse settings. In this article, we delve into the challenges faced and strategies employed when incorporating AGVs for efficient warehouse automation across diverse environments.
Contents
Understanding AGVs and Their Applications
So, what’s AGVs? Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and navigation systems, AGVs are revolutionary self-driving vehicles that navigate warehouses independently. These intelligent robots possess the ability to perform a multitude of tasks, including but not limited to material handling, inventory management, picking items, and transporting goods. Whether it’s a vast distribution center or a compact warehouse space, AGVs are meticulously designed to operate seamlessly in various environments.
Assessing Warehouse Environments
Implementing AGVs in different warehouse environments requires careful consideration of various factors. Take into account the following elements when adapting to different environments:
- Warehouse Layout and Infrastructure: Assess the layout of the warehouse, which includes considering aisle widths, rack heights, and column placements. AGVs need sufficient space to navigate safely and effectively. Modify the infrastructure by incorporating designated AGV lanes, installing charging stations, or adjusting storage racks to accommodate AGV operations.
- Floor Conditions: The condition of warehouse floors can vary in terms of texture, levelness, and traction. Since AGVs rely on their wheels for movement, it is crucial to ensure that floor conditions are suitable for smooth and reliable navigation. Conduct thorough floor assessments and address any repairs or modifications required to optimize AGV performance.
- Traffic Flow and Obstacles: Analyze the flow of traffic within the warehouse environment, including movement patterns of personnel, forklifts, and other equipment. Programming your AGVs to navigate efficiently through high-traffic areas while avoiding collisions is essential. Identify potential obstacles like protruding objects or temporary obstructions in order to implement measures that enable obstacle detection and avoidance strategies.
Customizing AGVs for Specific Environments
AGVs can be customized or specialized for different warehouse settings, accommodating their unique requirements effectively.
- Customized Payload Capacity: AGVs can be tailored to handle diverse payload capacities according to the specific needs of the warehouse. This customization guarantees that AGVs are equipped to transport goods of various sizes and weights, thereby optimizing material handling efficiency to its fullest potential.
- Navigation Adaptation: Depending on the environment’s characteristics, AGVs can utilize different navigation systems for optimal performance. Well-defined and structured environments may benefit from laser-guided systems, while dynamic and less structured environments may require vision-based systems that adapt as necessary. Choose a navigation system that fits well with the layout and conditions of your warehouse setting.
- Prioritize Safety: Ensure personnel safety and smooth warehouse operations by integrating crucial safety features into AGVs. Proximity sensors, emergency stop buttons, and audible alarms could be incorporated into AGV design to alert workers when an AGV approaches nearby areas. Establish clear safety protocols and communicate them effectively to all employees working alongside AGVs for heightened awareness and precautions
Integration and Scalability
For successful warehouse automation utilizing AGVs, it is crucial to smoothly merge them into current systems. This involves establishing a connection between AGVs and either the Warehouse Management System or Warehouse Control System. Such integration allows for effective real-time communication, task distribution, and optimization.
Moreover, when implementing AGV technology, it’s important to consider scalability in relation to future growth and expansion of the warehouse. Therefore, designing AGV fleets that can adapt to increasing demands is essential — these fleets should have the capability to effortlessly integrate additional AGVs into the preexisting system.
Conclusion
In the realm of warehouse automation, AGVs have become an absolute necessity. They work wonders by streamlining operations and boosting efficiency. It is essential to evaluate various factors when implementing AGVs in different warehouse environments, such as the layout of the space, condition of the flooring, and patterns of traffic. By customizing AGVs to handle specific tasks and carry suitable loads, their flexibility and adaptability can be further improved.
To ensure a seamless transition and facilitate future growth, integrating AGVs with existing systems while considering scalability is vital. Each environment presents unique challenges that need careful consideration and proper solutions. Only then can warehouses fully unleash the potential power of AGVs and enjoy heightened productivity in their automated operations.


































 Online casino
Online casino
