Maintenance has long ceased to be considered a mere factor of costs. Effective and efficient maintenance provides an important advantage over the competition in the productive sector. With the reduction of time and stock margins, and with JIT * / JIS * logistics strategies, downtime has become very important and can lead to serious production losses (Just in time, Just in sequence)
The approach of an adequate maintenance strategy is a topic of increasing importance in which the management of the company should be involved since its integration in corporate processes and strategies is decisive for corporate success.
The main sources of losses in maintenance are:
– Installation stops
– Loss of time linked to the preparation of equipment
– Operation without load and brief stops
– Working sequences at a reduced pace
– Difficulties associated with the start-up
– Losses of quality
Maintenance strategies
Definition of the objectives of the company in relation to maintenance
In many publications, concepts such as ‘autonomous maintenance’ are often confused or terms such as ‘maintenance’ and ‘routine maintenance’ are used interchangeably. These concepts are clarified below. According to DIN 31051, maintenance is the set of activities developed in order to preserve or restore the ideal situation, as well as those used for the determination and evaluation of the real situation of a system.
These measures are divided into four basic categories:
– Routine maintenance
– Inspection
– Repair
– Elimination of weak points or correction
Based on the strategy and the definition of basic competencies, it is decided which of these activities can be outsourced.
In most cases, autonomous maintenance is limited to cleaning and lubricating equipment. The inspection of the facilities does not include, however, maintenance of repair. The definition of the TPM must be consistent with the philosophy: ‘Total Productive Maintenance or Total Productive Management?’
The different methods and/or maintenance strategies are described in more detail below.
Corrective maintenance: reactive maintenance, repair after a breakdown, rectification of breakdowns. Repair of faults.
– Advantage: The equipment is rushed to the maximum until the margin of use is exhausted; little expense for maintenance until the machine breaks down.
– Disadvantage: Higher costs due to unforeseen downtime or the need to perform overtime, purchase of spare parts (delivery by taxi), extraordinary shifts. An option, when possible, is to look for alternative facilities, modify existing ones, etc.
Preventive maintenance: Routine verification activities at predetermined intervals. Scheduled and standardized maintenance at regular intervals (depending on the wear of the components, load curves).
Advantage: Unforeseen downtime is reduced.
Disadvantage: Greater deployment of personnel; high costs of spare parts, since parts with little wear are also replaced; danger of falling into an ‘excess of maintenance’. It is advisable to question the interval planning during the operating time of the installations according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
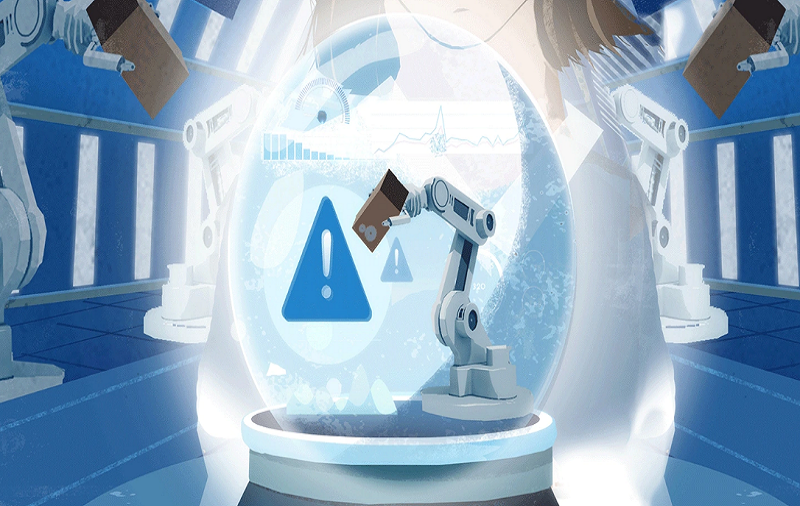
Condition based maintenance (according to condition of the machine or installation)
The maintenance management software is based on the determination of the right moment (variable) to carry out the necessary measurements based on the recorded and available data (inspection, measurements). It is based on the use of techniques for registering parameters and on the state of the piece or component. This implies a permanent control of the machinery (for example, diagnosis of vibrations, thermography or measurement of the consumption of current or compressed air, in addition to checking leaks and fissures, flow rate or endoscopy). This ensures the replacement of defective components if necessary, in order to avoid economic losses due to inactivity.
Advantages: optimal control of the wear margin of the relevant components, continuous observation of the operating status. The permanent supervision allows to identify in time any damage in the components, with what increases the useful life so much of the components as of the machines.
Disadvantage: this method has its limits; the costs of acquisition and training can be very high. In some cases, very expensive and complex diagnostic systems are required, which are also only applicable in a limited way. In short: the cost can exceed the expected savings.
Conclusion:
The effective utility of a maintenance system based on the state of the machine is evident in the aging phase. Due to the normal wear and tear of a production facility over time, faults also affect fundamental components for the operation of the same, such as chains, bearings, guides, electrical components, etc.






















![GTA Vice City APK Download for Android Free +OBB+ Mod [2023] GTA Vice City](https://www.mobupdates.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/GTA-Vice-City-100x70.png)








 Online casino
Online casino
